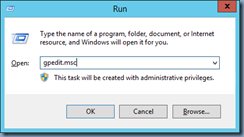
One of the questions I get asked most frequently about Lync Server 2013 is how to configure the integration with Exchange 2010 OWA so users can use the Outlook Web App for IM because most of the material out there on the web were written for Lync Server 2010 and Exchange Server 2010. The short answer is that nothing has really changed so the instructions provided for Lync Server 2010 would actually work for Lync Server 2013 but since I’ve had to walk through a lot of people on the process, I thought I’d write a blog post to demonstrate it.
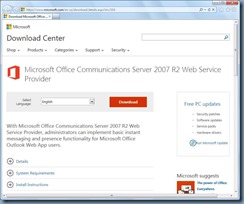
Step #1 – Download Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007 R2 Web Service Provider onto CAS Server or Servers
Begin by downloading the following bundle:
Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007 R2 Web Service Provider
https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/download/details.aspx?id=2310
The downloaded file should be named CWAOWASSPMain.msi with a size of 10,642KB:
Step #2 – Download Patches (UcmaRedist.msp and CWAOWASSP.msp)
Next, download the following patch:
Unified Communications Managed API 2.0 Redist (64 Bit) Hotfix KB 2647091
http://www.microsoft.com/en-us/download/details.aspx?id=7557
The downloaded file should be named UcmaRedist.msp with a size of 4,132KB:
Download the following patch:
OCS 2007 R2 Web Service Provider Hotfix KB 981256
http://www.microsoft.com/en-us/download/details.aspx?id=797
The downloaded file should be named CWAOWASSP.msp with a size of 136KB:
Step #3 – Run CWAOWASSPMain.msi
Proceed by running the CWAOWASSPMain.msi file:
Once completed, you will notice the following line item in the Programs and Features:
Step #4 – Run CWAOWASSP.msi, dotnetfx35setup.exe, UcmaRedist.msi, and vcredist_x64x.exe installed by CWAOWASSPMain.msi
What the CWAOWASSPMain.msi file does is actually place 4 files into the folder specified during the wizard so continue by browsing to that folder:
… then install the following:
vcredist_x64.exe
Note the following item in the Programs and Features:
Microsoft Visual C++ 2008 Redistributable – x64 9.0.21022
Depending on whether .NET 3.5 is already installed on the server, you may not need to install the following:
donetfx35setup.exe
Next, install the following:
UcmaRedist.msi
Note that this is a silent install so you won’t see any prompts.
Once completed, you should see the following line item in the Programs and Features:
Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007 R2, Microsoft Unified Communications Managed API 2.0 Core Redist 64-bit
Finally, install the last msi:
CWAOWASSP.msi
Note that this is also a silent install:
If you forgot to run UCMARedist.msi first then you would receive the following message:
Microsoft Office Communicaions Server 2007 R2. Web Service Provider installation requires that Microsoft Unified Communications Managed API 2.0 Core Redist 64-bit is already installed. Either use Setup.exe for installation or run UCMARedist.msi included with the product to install the redistributable.
The following line item will be displayed in the Programs and Features once the install has completed:
Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007 R2, Web Service Provider
Step #5 – Patch the components install in Step #4
Proceed by navigating back to the packages downloaded in Step #2 and patch UcmaRedist.msi from 3.5.6907.0 to Microsoft Office Communciations Server 2007 R2, Microsoft Unified Communications Managed API 2.0 Core Redist 64-bit from 3.5.6907.0 to 3.5.6907.244:
Note the version change to 3.5.6907.244:
Continue by patching CWAOWASSP.msp from 3.5.6907.57 to Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007 R2, Web Service Provider 3.5.6907.202:
Note the version change to 3.5.6907.202:
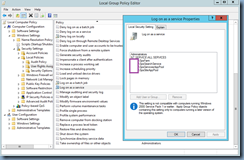
Step #6 – Configuring the Exchange 2010 CAS Server
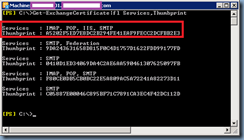
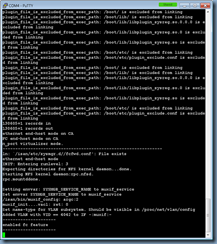
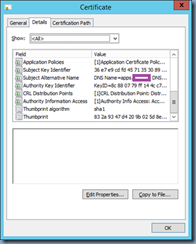
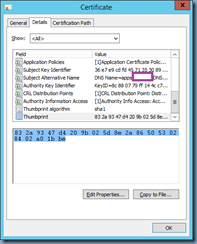
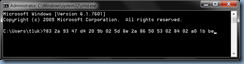
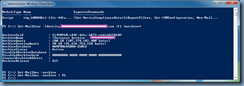
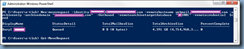
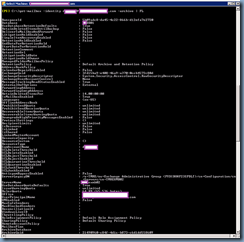
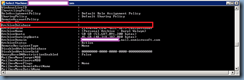
With the components installed onto your CAS server or servers, proceed by launching the Exchange Management Shell and identify the certificate that is currently assigned to the IIS server. Run the following cmdlet to get the list of certificates currently used by the Exchange CAS server:
Get-ExchangeCertificate|fl Services,Thumbprint
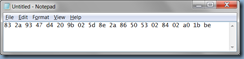
Note that the Exchange CAS server used in this example actually has multiple certificates for different services but the one we are interested in is the one used for the IIS service:
Copy the Thumprint of the certificate to Notepad.
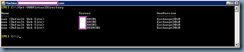
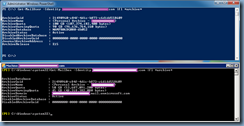
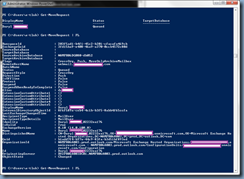
There will be environments when multiple OWA Virtual Directories are configured on the the Exchange Server so to check simply execute the Get-OWaVirtualDirectory cmdlet and verify that the only returned result is owa (Default Web site):
Get-OWAVirtualDirectory
Another cmdlet we can execute to display the virtual directory mapped to OWA is the following:
Get-OwaVirtualDirectory | Where-Object {$_.ExternalUrl -eq https://webmail.domain.com/owa}
Note that we only have one single OWA Virtual Directory in the example above so we won’t have to specifically target the virtual directory with the -identity switch but I like to be safe so I use the Where-Object {$_.ExternalUrl -eq https://webmail.domain.com/owa} anyways. Continue by executing the following to configure the InstantMessaging parameters of the virtual directory:
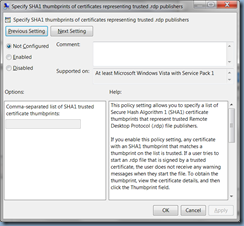
Get-OwaVirtualDirectory | Where-Object {$_.ExternalUrl -eq "https://webmail.domain.com/owa"} | Set-OwaVirtualDirectory -InstantMessagingType OCS -InstantMessagingEnabled:$true -InstantMessagingCertificateThumbprint A5202F5ED7E8DC2B294FE41EAF9FECC2DCFBB2E3 -InstantMessagingServerName <FQDNofLyncSTDserverOrPool>
Note that when you execute the following cmdlet, you will see the parameters assigned:
Get-OwaVirtualDirectory | Where-Object {$_.ExternalUrl -eq "https://webmail.domain.com/owa"} | FL Server,Instant*
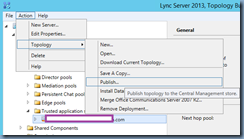
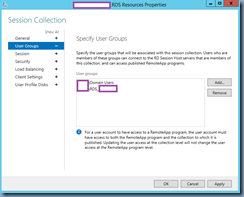
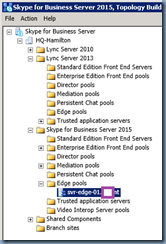
Step #7 – Configure the Trusted Application Pool
Launch the Lync Server 2013 Topology Builder tool, navigate to Lync Server > Datacenter > Lync Server 2013 > Trusted application servers then right click on the node and create a New Trusted Application Pool…:
The Exchange topology in this example contains 2 CAS servers so I’ll be using the Multiple computer pool option with the webmail URL as the pool FQDN matching the certificate name:
Add the individual CAS server names into the Define the computers in this pool step:
Associate the next hop server as the front end server:
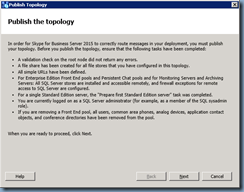
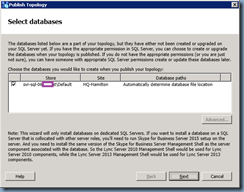
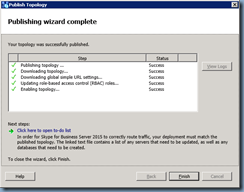
Publish the topology:
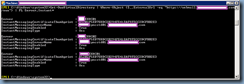
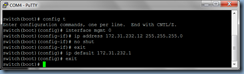
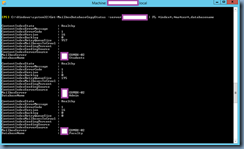
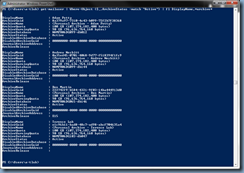
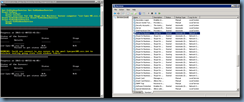
Next, verify that the changes are in place by launching the Lync Server Management Shell and executing the following cmdlet:
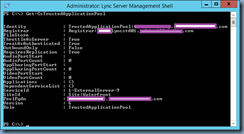
Get-CsTrustedApplicationPool
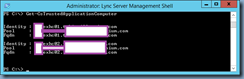
Execute the follow cmdlet to verify the computers defined in the pool:
Get-CsTrustedApplicationComputer
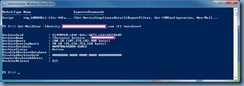
With the configuration settings verified, proceed by using the cmdlet New-CsTrustedApplication cmdlet to define a trusted application and associate it to the new trusted application pool.
A free port will need to be identified and then used to assign as the listening port on the Lync server. Jeff Schertz’s Lync 2010 with Exchange 2010 integration (http://blog.schertz.name/2010/11/lync-and-exchange-im-integration/) provides an easy way to determine whether a port is free and that is to use the command:
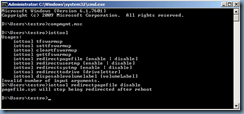
netstat -a | findstr <port #>
We can use either 5059 as Jeff demonstrates or another one that is free. For the purpose of this example, we’ll use 5059:
With the port identified, execute the following cmdlet to create the new trusted application and associate the CAS array to it:
New-CsTrustedApplication -ApplicationId ExchangeOWA -TrustedApplicationPoolFqdn <casArrayFQDN> -Port 5059
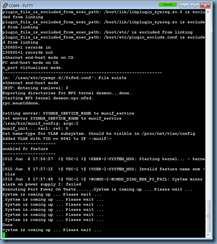
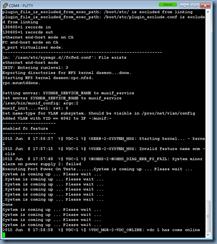
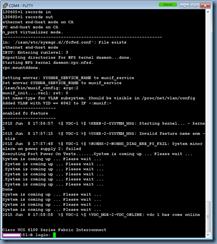
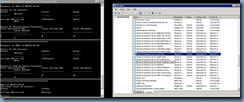
Enable the topology with the following cmdlet:
Enable-CsTopology -v
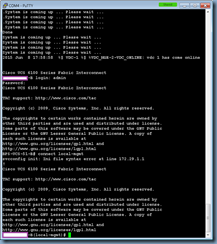
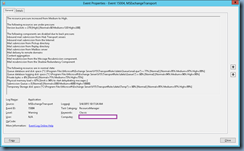
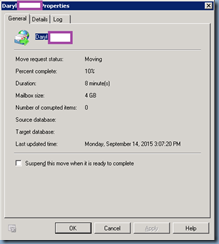
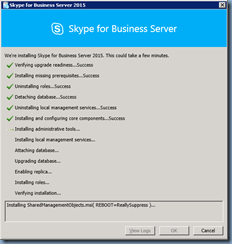
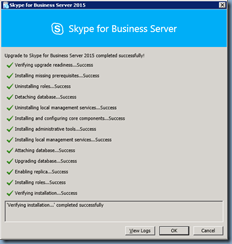
Once the publishing completes, you can review the logs to ensure there are no unexpected warnings or errors:
That’s it. You should be able to log into Outlook Web App and see your Lync presence at the top right hand corner and your contact list on the left hand pane.
![clip_image002[5] clip_image002[5]](http://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-BHPhJnV1e3E/VXQ2XiJGIpI/AAAAAAAB50A/ZyTKmqNzgSk/clip_image0025_thumb1.jpg?imgmax=800)
![clip_image002[7] clip_image002[7]](http://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-ypc69wmqopc/VXQ2ZoSPTzI/AAAAAAAB50Q/3yez7gQNnXc/clip_image0027_thumb1.jpg?imgmax=800)
![clip_image002[9] clip_image002[9]](http://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-oDZYWsAUK-o/VXQ2a9M-3HI/AAAAAAAB50g/kCfUlrodu0M/clip_image0029_thumb%25255B1%25255D.jpg?imgmax=800)
![clip_image002[11] clip_image002[11]](http://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-xbathv0y_EA/VXQ2ciEhXMI/AAAAAAAB50w/HoJiq510Gz4/clip_image00211_thumb1.jpg?imgmax=800)
![clip_image002[13] clip_image002[13]](http://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-xv4b7wzDBYA/VXQ2edzM8hI/AAAAAAAB51A/7ZQOGVozIhw/clip_image00213_thumb%25255B1%25255D.jpg?imgmax=800)
![clip_image002[15] clip_image002[15]](http://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-Sa8J_CfhC9o/VXQ2fxS3rlI/AAAAAAAB51Q/1KWjsN5vfRw/clip_image00215_thumb%25255B1%25255D.jpg?imgmax=800)
![clip_image002[17] clip_image002[17]](http://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-dIyteGcObAk/VXQ2hGMyCgI/AAAAAAAB51g/6HLK2aisgsM/clip_image00217_thumb.jpg?imgmax=800)
![clip_image002[19] clip_image002[19]](http://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-nHYKUea96Qs/VXQ2j0m8giI/AAAAAAAB51w/-_Hxi15fdDc/clip_image00219_thumb.jpg?imgmax=800)
![clip_image002[21] clip_image002[21]](http://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-Mz_mP22o--o/VXQ2lOTsCHI/AAAAAAAB52A/xD40oJVazyM/clip_image00221_thumb.jpg?imgmax=800)
![clip_image002[23] clip_image002[23]](http://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-bQetRP8_504/VXQ2msRkP3I/AAAAAAAB52Q/eYA4bcGzI38/clip_image00223_thumb.jpg?imgmax=800)
![clip_image002[25] clip_image002[25]](http://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-aG80qAb4EK0/VXQ2oQ7dJKI/AAAAAAAB52g/LLisS-OhqhM/clip_image00225_thumb1.jpg?imgmax=800)
![clip_image002[27] clip_image002[27]](http://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-WnKBgyhXDCc/VXQ2pqdMLjI/AAAAAAAB52w/ljRCLZgxkp8/clip_image00227_thumb1.jpg?imgmax=800)
![clip_image002[29] clip_image002[29]](http://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-5zqxMnHnNME/VXQ2rJninDI/AAAAAAAB53A/lmrUwYIWH30/clip_image00229_thumb.jpg?imgmax=800)
![clip_image002[33] clip_image002[33]](http://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-WYNQXIP_l7A/VXQ2thYkNbI/AAAAAAAB53Q/asStvHvFVS8/clip_image00233_thumb.jpg?imgmax=800)
![clip_image002[35] clip_image002[35]](http://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-y641LSaH0SA/VXQ2vXwIM7I/AAAAAAAB53g/VOp60ctX370/clip_image00235_thumb.jpg?imgmax=800)
![clip_image002[37] clip_image002[37]](http://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-du23WVqIGNU/VXQ2w-DZR3I/AAAAAAAB53w/k9MMwYlCjU4/clip_image00237_thumb.jpg?imgmax=800)
![clip_image002[39] clip_image002[39]](http://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-u1YmLMPrRV0/VXQ2y7ZCwVI/AAAAAAAB54A/8zrYHjIZMQg/clip_image00239_thumb.jpg?imgmax=800)
![clip_image002[41] clip_image002[41]](http://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-37osRuihKHY/VXQ20mpBKZI/AAAAAAAB54Q/onm1BhzaHxY/clip_image00241_thumb1.jpg?imgmax=800)
![clip_image002[43] clip_image002[43]](http://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-C2lRuJ1DTKs/VXQ219tU6yI/AAAAAAAB54g/Hc-m78sxo5g/clip_image00243_thumb.jpg?imgmax=800)
![clip_image002[45] clip_image002[45]](http://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-KnBisdyeGrQ/VXQ23sudTmI/AAAAAAAB54w/cYx2hCz7isw/clip_image00245_thumb.jpg?imgmax=800)
![clip_image002[47] clip_image002[47]](http://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-m7AkEhYMbb8/VXQ25CBTY-I/AAAAAAAB55A/3kXb2SHKd9g/clip_image00247_thumb.jpg?imgmax=800)
![clip_image002[49] clip_image002[49]](http://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-psfVVpNQ-Pg/VXQ26vPy6aI/AAAAAAAB55Q/QHLFAhoaGZQ/clip_image00249_thumb.jpg?imgmax=800)
![clip_image002[51] clip_image002[51]](http://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-UBQ50O8ndEM/VXQ28R58N1I/AAAAAAAB55g/0DTAOsQTEoY/clip_image00251_thumb1.jpg?imgmax=800)
![clip_image002[53] clip_image002[53]](http://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-LC_P4M-4sQ8/VXQ29wnMHgI/AAAAAAAB55w/nM9EzAqStP4/clip_image00253_thumb.jpg?imgmax=800)
![clip_image002[55] clip_image002[55]](http://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-IFTzRw_aNa8/VXQ2_UfWPzI/AAAAAAAB56A/T2Njebv-07Y/clip_image00255_thumb.jpg?imgmax=800)
![clip_image002[59] clip_image002[59]](http://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-RZVEOGzkkQI/VXQ3Ayoqa_I/AAAAAAAB56Q/G3GEcRsjpcs/clip_image00259_thumb.jpg?imgmax=800)
![clip_image002[57] clip_image002[57]](http://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-rWZbinpstf0/VXQ3CqMqY6I/AAAAAAAB56g/kM7lqRS7IWM/clip_image00257_thumb1.jpg?imgmax=800)
![clip_image002[61] clip_image002[61]](http://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-0tltuteXd6k/VXQ3EU5w-jI/AAAAAAAB56w/B_tBrbiEcjU/clip_image00261_thumb1.jpg?imgmax=800)
![clip_image002[63] clip_image002[63]](http://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-q5sX80RmyJk/VXQ3F6nhe6I/AAAAAAAB57A/-NNE5dhEXsQ/clip_image00263_thumb.jpg?imgmax=800)
![clip_image002[65] clip_image002[65]](http://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-ZZBXOw4OIZE/VXQ3Hf-_8RI/AAAAAAAB57Q/fBzaJ3VEi-s/clip_image00265_thumb.jpg?imgmax=800)
![clip_image002[67] clip_image002[67]](http://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-idwsRASAPRM/VXQ3JPeUGoI/AAAAAAAB57g/fLNVYCXMIN8/clip_image00267_thumb.jpg?imgmax=800)
![clip_image002[69] clip_image002[69]](http://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-OWIHQ8d8ivg/VXQ3KuVWGII/AAAAAAAB57w/5nAUQxqQu88/clip_image00269_thumb.jpg?imgmax=800)
![clip_image002[71] clip_image002[71]](http://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-x3neBll60_w/VXQ3MHWJrnI/AAAAAAAB58A/w_7Ly0B-9wE/clip_image00271_thumb.jpg?imgmax=800)
![clip_image002[73] clip_image002[73]](http://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-YQgIxt2tRC8/VXQ3N5_bzaI/AAAAAAAB58Q/pQrKWxWyTPs/clip_image00273_thumb.jpg?imgmax=800)
![clip_image002[75] clip_image002[75]](http://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-7XGhiI2IUzg/VXQ3PHzL-SI/AAAAAAAB58g/C5l9JMiDsj8/clip_image00275_thumb.jpg?imgmax=800)
![clip_image002[77] clip_image002[77]](http://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-JUveuzeyy-U/VXQ3QsN9D6I/AAAAAAAB58w/4o9W8A07_j4/clip_image00277_thumb.jpg?imgmax=800)
![clip_image002[79] clip_image002[79]](http://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-r9Cf-bYa2js/VXQ3SeDnbdI/AAAAAAAB59A/EqK2ussMhCQ/clip_image00279_thumb1.jpg?imgmax=800)


![clip_image002[1] clip_image002[1]](http://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-F_OnrkiwV4s/VXQ3bB5uRsI/AAAAAAAB5-g/zv2oax4Cs6o/clip_image0021_thumb1.jpg?imgmax=800)
![clip_image002[3] clip_image002[3]](http://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-pcen7fPx8zg/VXQ3cvkXY9I/AAAAAAAB5-w/f42IE8DtkHE/clip_image0023_thumb.jpg?imgmax=800)
![clip_image002[5] clip_image002[5]](http://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-EXt7xha5J1k/VXQ3eJc2qcI/AAAAAAAB5_A/EAOYp0Zc2iQ/clip_image0025_thumb.jpg?imgmax=800)
![clip_image002[7] clip_image002[7]](http://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-KWI9km8KO0w/VXQ3ftKxp7I/AAAAAAAB5_Q/TCncVcX89a0/clip_image0027_thumb.jpg?imgmax=800)


![clip_image002[9] clip_image002[9]](http://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-taGMrPmOZWs/VXQ3lTURBuI/AAAAAAAB6AQ/NQgSj_tX0NU/clip_image0029_thumb.jpg?imgmax=800)
![clip_image002[11] clip_image002[11]](http://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-w0gJKO3-HS0/VXQ3pwwyN6I/AAAAAAAB6BA/0o5ynf78eFM/clip_image00211_thumb.jpg?imgmax=800)

![clip_image002[13] clip_image002[13]](http://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-g_yvm_F8hPU/VXQ3s9rimmI/AAAAAAAB6Bg/3iXmzyBz3o0/clip_image00213_thumb.jpg?imgmax=800)
![clip_image002[15] clip_image002[15]](http://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-3v7oDdL1aJY/VXQ3ucBoCHI/AAAAAAAB6Bw/8U-xNanWGPE/clip_image00215_thumb.jpg?imgmax=800)
























![clip_image002[4] clip_image002[4]](http://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-82HasQgmWYU/VaAc2M-bdfI/AAAAAAAB6Tw/u8HPw7dA8e4/clip_image002%25255B4%25255D_thumb%25255B2%25255D.jpg?imgmax=800)











































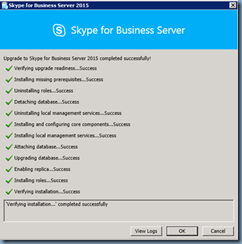


![clip_image002[4] clip_image002[4]](http://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-O6uqTp-Ytp8/VkHrUEP7w1I/AAAAAAAB63Q/PIsNDtplqkQ/clip_image0024_thumb.jpg?imgmax=800)
![clip_image002[6] clip_image002[6]](http://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-WmxQnasHy54/VkHrZAMfdkI/AAAAAAAB63g/edxZymRJBAA/clip_image0026_thumb.jpg?imgmax=800)
![clip_image002[8] clip_image002[8]](http://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-dWewpelu6Fc/VkHrehMQGfI/AAAAAAAB63w/eHOM6CRWEPk/clip_image0028_thumb.jpg?imgmax=800)
![clip_image002[10] clip_image002[10]](http://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-FKVXVL_G9Sk/VkHrj2nCd8I/AAAAAAAB64A/BgKKWzu23SY/clip_image00210_thumb.jpg?imgmax=800)
![clip_image002[12] clip_image002[12]](http://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-umPfn4nCRRA/VkHrpqrIK5I/AAAAAAAB64Q/SSbrTc5BWBk/clip_image00212_thumb.jpg?imgmax=800)
![clip_image002[14] clip_image002[14]](http://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-fhVJsqEDKRI/VkHrvOjdENI/AAAAAAAB64c/D8S2-VR49-o/clip_image00214_thumb.jpg?imgmax=800)
![clip_image002[16] clip_image002[16]](http://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-6o2Z_RY2gl4/VkHr0bWcuWI/AAAAAAAB64o/lGkm85hVimE/clip_image00216_thumb.jpg?imgmax=800)

![clip_image002[18] clip_image002[18]](http://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-aTG4HGx_nig/VkHr_cRNEmI/AAAAAAAB65Q/qU7vuYbCo_o/clip_image00218_thumb.jpg?imgmax=800)
![clip_image002[20] clip_image002[20]](http://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-Sc25PjCmG1A/VkHsEbN98AI/AAAAAAAB65g/lnS_7Nz1Ejg/clip_image00220_thumb.jpg?imgmax=800)
![clip_image002[22] clip_image002[22]](http://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-sSmwkKXKwJk/VkHsJntKAoI/AAAAAAAB65s/hWtU9e_kGw8/clip_image00222_thumb.jpg?imgmax=800)
![clip_image002[24] clip_image002[24]](http://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-zGdOE7TWNw8/VkHsPLdNknI/AAAAAAAB66A/fUFaOlkKfzY/clip_image00224_thumb.jpg?imgmax=800)
![clip_image002[26] clip_image002[26]](http://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-wG1nmcVBqxg/VkHsUqhKCqI/AAAAAAAB66M/FMVJ_PtNjZ8/clip_image00226_thumb.jpg?imgmax=800)
![clip_image002[28] clip_image002[28]](http://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-Ee0Db6kMieM/VkHsZyVef9I/AAAAAAAB66g/Oe8CkfkGVvs/clip_image00228_thumb.jpg?imgmax=800)
![clip_image002[30] clip_image002[30]](http://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-JeppdrwkMEg/VkHsfDe5uzI/AAAAAAAB66w/WkGNFwBS224/clip_image00230_thumb.jpg?imgmax=800)
![clip_image002[32] clip_image002[32]](http://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-c1NEJ4ddmio/VkHskQmnNvI/AAAAAAAB67E/03jGas2pnJ4/clip_image00232_thumb.jpg?imgmax=800)
![clip_image002[34] clip_image002[34]](http://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-LGej8xDjDIs/VkHspggqUrI/AAAAAAAB67U/Gn8PsiMa4bU/clip_image00234_thumb1.jpg?imgmax=800)
![clip_image002[36] clip_image002[36]](http://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-K94zbPJQ6cM/VkHsuGEWCCI/AAAAAAAB67k/z_GbJntj2MA/clip_image00236_thumb1.jpg?imgmax=800)
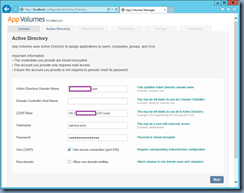

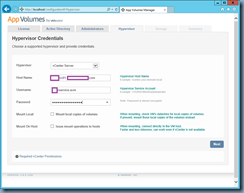



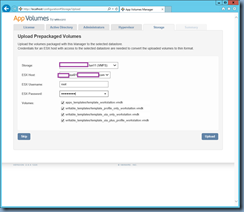

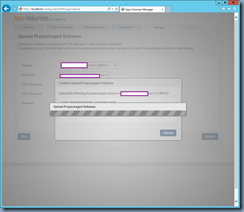

![clip_image002[1] clip_image002[1]](http://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-VBOzqiBmfYc/VkHtobR1MmI/AAAAAAAB6-U/49pgTONj_zA/clip_image0021_thumb1.jpg?imgmax=800)
![clip_image002[4] clip_image002[4]](http://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-DkUFA4weI2c/VkM7zbyo2DI/AAAAAAAB6-8/nH51of_4blk/clip_image0024_thumb.jpg?imgmax=800)
![clip_image002[6] clip_image002[6]](http://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-m2JkF_XBtg0/VkM74gIaf0I/AAAAAAAB6_M/nC8nM4KgGjc/clip_image0026_thumb.jpg?imgmax=800)
![clip_image002[8] clip_image002[8]](http://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-O_vZXyUfLqI/VkM79l2iAvI/AAAAAAAB6_c/2CkgMB3cv4E/clip_image0028_thumb.jpg?imgmax=800)
![clip_image002[10] clip_image002[10]](http://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-pebcR09t5SQ/VkM8C5yYzsI/AAAAAAAB6_s/pdFpt0HsVU0/clip_image00210_thumb.jpg?imgmax=800)
![clip_image002[12] clip_image002[12]](http://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-uIMy84idx3c/VkM8H-yvXgI/AAAAAAAB6_8/yCtzoQQaKrk/clip_image00212_thumb.jpg?imgmax=800)
![clip_image002[14] clip_image002[14]](http://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-eY1qo4F7-cw/VkM8NEJwblI/AAAAAAAB7AM/R6ed_HPCpVw/clip_image00214_thumb.jpg?imgmax=800)
![clip_image002[16] clip_image002[16]](http://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-B_5vujf8lyY/VkM8ScYDffI/AAAAAAAB7Ac/J1f7SVn1OjM/clip_image00216_thumb.jpg?imgmax=800)
![clip_image002[18] clip_image002[18]](http://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-OKnAQyydGhw/VkM8YN4W63I/AAAAAAAB7As/gIMCJoAd4Pw/clip_image00218_thumb.jpg?imgmax=800)
![clip_image002[22] clip_image002[22]](http://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-nL7boBYWAxI/VkM8dDKKDPI/AAAAAAAB7A8/mG-OSZx5F4E/clip_image00222_thumb.jpg?imgmax=800)
![clip_image002[20] clip_image002[20]](http://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-80ruBMRYVeg/VkM8iaZwSDI/AAAAAAAB7BM/w5eVWBqi934/clip_image00220_thumb.jpg?imgmax=800)
![clip_image002[24] clip_image002[24]](http://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-Yvz8jcmS06g/VkM8n5eigeI/AAAAAAAB7Bc/sqhH8FoWmXw/clip_image00224_thumb1.jpg?imgmax=800)





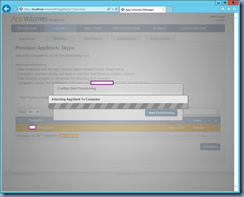
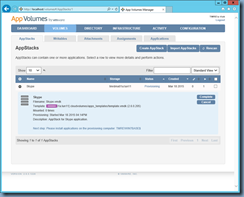
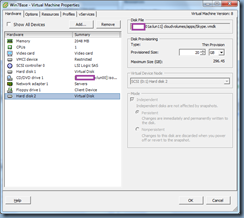
![clip_image002[30] clip_image002[30]](http://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-0S_WYG0ltfY/VkM9kOKrO2I/AAAAAAAB7Eg/_NIlEX-mEJs/clip_image00230_thumb1.jpg?imgmax=800)
![clip_image002[32] clip_image002[32]](http://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-OZjqV9qq01w/VkM9o-xirzI/AAAAAAAB7Ew/__vEGo-Hctw/clip_image00232_thumb1.jpg?imgmax=800)
![clip_image002[34] clip_image002[34]](http://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-yzw7IZ7PhPs/VkM9tnn_HwI/AAAAAAAB7FA/4KWhCwj6Ec0/clip_image00234_thumb.jpg?imgmax=800)
![clip_image002[36] clip_image002[36]](http://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-Oyu4gD8MNcE/VkM9ydSDohI/AAAAAAAB7FU/NMohEsTnKtE/clip_image00236_thumb1.jpg?imgmax=800)
![clip_image002[38] clip_image002[38]](http://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-8mJmB3jEl0g/VkM93WQPP6I/AAAAAAAB7Fk/AwCMMGQfFHQ/clip_image00238_thumb1.jpg?imgmax=800)

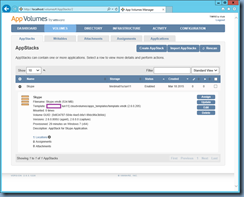
![clip_image002[40] clip_image002[40]](http://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-ezqTCG0IsWo/VkM-Fi9IqsI/AAAAAAAB7GQ/5CYELpYrh6U/clip_image00240_thumb1.jpg?imgmax=800)




![clip_image002[42] clip_image002[42]](http://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-fFolKqH5f9c/VkM-o6bMPlI/AAAAAAAB7IE/CfUfWQMIu6U/clip_image00242_thumb1.jpg?imgmax=800)
![clip_image002[4] clip_image002[4]](http://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-qsYgPBTS5uE/VkSU4YzaSmI/AAAAAAAB7JQ/fTkuSI58qvY/clip_image0024_thumb1.jpg?imgmax=800)
![clip_image002[6] clip_image002[6]](http://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-Drx8IamKAeY/VkSVCRPZhfI/AAAAAAAB7Js/EDThXYsWh48/clip_image0026_thumb1.jpg?imgmax=800)


![clip_image002[8] clip_image002[8]](http://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-ICet0O7h14c/VkSVcA2LBHI/AAAAAAAB7K8/bdnot4gAaWk/clip_image0028_thumb1.jpg?imgmax=800)
![clip_image002[10] clip_image002[10]](http://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-T97TOYOBqfc/VkSVhSE7QQI/AAAAAAAB7LM/mfYg1iXXFQQ/clip_image00210_thumb1.jpg?imgmax=800)
![clip_image002[12] clip_image002[12]](http://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-CqIAbhkOF-4/VkSVmksa9rI/AAAAAAAB7Lc/4nq37xFznoM/clip_image00212_thumb1.jpg?imgmax=800)
![clip_image002[14] clip_image002[14]](http://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-_E9xCV1t1-o/VkSVrgbNm5I/AAAAAAAB7Lw/jXYXiyHy-F8/clip_image00214_thumb1.jpg?imgmax=800)
![clip_image002[16] clip_image002[16]](http://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-khP-6a3TnfQ/VkSVwhRcuFI/AAAAAAAB7MA/NBO63GnvjMI/clip_image00216_thumb1.jpg?imgmax=800)
![clip_image002[18] clip_image002[18]](http://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-nFzjO3Q0a5w/VkSV1iZfXDI/AAAAAAAB7MQ/RAuLpefECho/clip_image00218_thumb1.jpg?imgmax=800)